As a professional, you experienced struggles with missed deadlines, were unclear about what priority to give, and had misalignment with teams. Agile Scrum is the savior that addresses these problems in your work environment.
After you get upskilled with this knowledge, you become a fully packed and market-ready professional with clearly defined roles, a habit of participating in regular planning, and attending review meetings.
In this article, you can understand Agile Scrum in just 15 minutes, giving you a quick, powerful insight into one of the most popular frameworks for managing projects effectively.
What Does “ Agile “Mean?
Agile is one of the project management approaches, which was introduced through “Agile Manifesto” in 2001 by a group of 17 software practitioners who discussed a lightweight method for software development as an alternative option of the traditional waterfall method at the Utah meeting in the USA.
Agile means the ability to think quickly, be mentally sharp. So those who follow this philosophy are generally called Agile thinkers or Agile Minds. In the context of business or project management, it means a flexible, iterative approach that gives priority to adapting to change and collaborating over traditional project methods’ rigid and linear plan.
In the last two decades, Agile has evolved into various methodologies and frameworks to fulfill the customized and changing needs of the market.
From its initial development and formalization, there are many types of Agile methodologies available in the market. Let’s see that in chronological order.
- 1991: Rapid Application Development (RAD)
- 1994: Dynamic Systems Development Method (DSDM)
- 1995: Scrum
- 1996: Extreme Programming & Crystal family of methodologies
- 1997: Feature-Driven Development (FDD)
- 2003: Lean Software Development
- 2003-2008: Kanban Adopted by Software Development
In this, Scrum is so popular, widely accepted, and recognized as an agile methodology, because of its first and most foundational principles. It has a quality of simplicity and structure that makes it effective for a variety of teams and projects.
The History of Scrum:
The Scrum framework was formally introduced to the public by Sutherland and Schwaber jointly presented the paper “The Scrum Development Process” at the OOPSLA conference in 1995. Later, Schwaber, with the help of Mike Cohn and Esther Derby, founded the Scrum Alliance as a non-profit organization to provide Certified Scrum Accreditation training programs to the public.
In 2009, they published a public document called “The Scrum Guide” to provide a definitive, minimalist, and widely accessible explanation of the Scrum Framework. Since its inception, this guide has been revised multiple times, with updates in 2011, 2013, 2016, 2017, and 2020.
What is Scrum? Why is Scrum a Popular Agile Framework?
Scrum is an agile framework used to manage projects. It assists teams in managing their daily work through a series of short, structured, timed cycles called Sprints. The Scrum Methodology has its own set of principles, values, and key components for the Scrum team to function.
Scrum Principles:
Scrum has its own set of principles that are:
- Empiricism and Lean Thinking: The decisions are made based on what is known and experienced. This helps to reduce waste and increase value.
To implement empiricism, one needs to follow below three pillars below,
- Transparency: Make all aspects of the process open to access (visible) to the persons who are involved in creating and working on the product development or projects.
- Inspection: Frequent checking on work and its progress helps to detect undesirable deviations of the project from its planned path.
- Adaptation: This ability to adjust as soon as possible if any inspection finds a deviation from the work. It’s the key characteristics of the agile work environment.
Scrum Values:
- Commitment: Every team member should give a pledge to attain the team’s goal and support each other.
- Courage: The boldness to do the right thing, work on tough problems, and be ready to face challenges.
- Focus: Focus on the Sprint goals and the work required to achieve them.
- Openness: the team should be open about their work, which creates transparency for each team member to get to know the progress.
- Respect: Respect for each team member creates a valuable workspace. Everyone’s skills and opinions have value in a collaborative environment.
How Scrum Team Works:
A Scrum team is small, cross-functional, self-managing people, generally consisting of a Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Developers to manage projects by applying its principles and values to deliver a valuable increment of the product each Sprint.
The entire Scrum process happened through these five time-boxed (time limit for each event) events:
- The Sprint: it’s the “container” of all the events. A fixed short period (1-4 weeks) where the team works to complete work prioritized in the product backlog and create a workable product increment. New Sprints start immediately after one ends. It’s a cyclic process.
- Product Backlog: A prioritized list of all the work needed for the product. The Product Owner manages this list.
- Sprint planning: It is the starting point of the Sprint to plan what to work on based on the product backlog list (Sprint Goal).
- Daily Scrum: A 15-minute daily short meeting for developers to inspect the process and accept the plan for the next 24 hours towards the Sprint goal. It is also called a “ Standup meeting, which happens daily at the same time.
- Sprint review: It’s conducted at the end of the Sprint to check the product. This is a collaborative meeting between the stakeholders and team members. Get feedback on what was built.
- Sprint Retrospective: This is also conducted at the end of the Sprint, like a lessons learned session. The team can discuss what went well, what could be improved, and create a plan for improvements in the next Sprint.
Beyond understanding Agile & Scrum, to begin your career in Scrum, you start by trying to get hands-on learning to showcase your expertise at another level. Choose Certified Scrum Master Certification, which opens tremendous career options in organizations worldwide that value Skilled Scrum Practitioners.
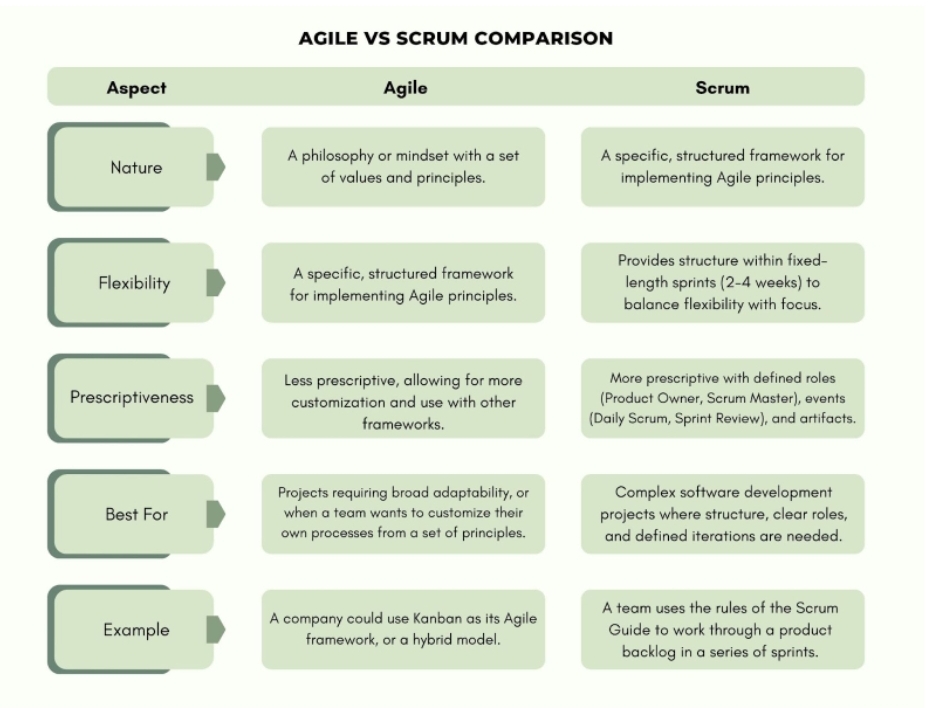
Agile Vs Scrum: Comparative Table
Many people confuse the two terms as being interchangeable somewhat externally; they look the same, but in the deeper sense, they are different. Agile is a broader philosophy, in that Scrum is one of the specific structured frameworks that place agile principles into practice.
Conclusion:
Agile is a good choice for a flexible, adaptable philosophy for various projects, while Scrum is better for complex software projects needing a structured framework with clear roles and processes.
If you are a professional handling software projects and complex initiatives, understanding agile and applying Scrum principles can transform the way you work.
It reduces confusion, gives you a clear path to achieve final objectives efficiently. Agile Scrum combo is a practical path to smarter, quicker, and at the same time, helps you achieve value delivery.








